What Term Refers to the Maximum Speed at Which Data Can Be Transferred?
Information technology Explained:
Bandwidth
What is bandwidth?
Bandwidth is measured as the amount of data that tin exist transferred from ane indicate to another within a network in a specific amount of time. Typically, bandwidth is expressed as a bitrate and measured in $.25 per 2nd (bps).
The term bandwidth refers to the transmission capacity of a connection and is an important gene when determining the quality and speed of a network or the internet connection.
There are several different ways to measure bandwidth. Some measurements are used to summate current data flow, while others measure maximum flow, typical period, or what is considered to exist good flow.
Bandwidth is also a key concept in several other technological fields. In signal processing, for example, it is used to draw the difference between the upper and lower frequencies in a transmission such as a radio bespeak and is typically measured in hertz (Hz).
Bandwidth tin be compared to water flowing through a pipe. Bandwidth would be the charge per unit at which water (data) flows through the pipe (connection) under various circumstances. Instead of $.25 per 2nd, we might mensurate gallons per minute. The amount of water that mayhap can catamenia through the pipe represents the maximum bandwidth, while the amount of h2o that is currently flowing through the pipe represents the current bandwidth.
Expressing bandwidth
Bandwidth was originally measured in $.25 per second and expressed as bps. However, today's networks typically accept much higher bandwidth than can be comfortably expressed by using such small units. Now it is common to encounter higher numbers that are denoted with metric prefixes, such equally Mbps, (megabits per 2d), Gbps (gigabits per 2nd), or Tbps (terabits per 2nd).
Thousand = kilo = i,000 bitsThousand = mega = 1,000 kilo = 1,000,000 bits
Thousand = giga = 1,000 mega = 1,000,000,000 bits
T = tera = i,000 giga = 1,000,000,000,000 $.25
Afterwards terabit, there are petabit, exabit, zettabit, and yottabit, each representing an additional power of 10.
Bandwidth tin also be expressed as bytes per second. This is commonly denoted with a capital B. For example, x megabytes per 2d would be expressed as 10 MB/southward or 10 MBps.
One byte is eight bits.
Thus, x MB/s = lxxx Mb/s.
The same metric prefixes can be used with bytes as with bits. Thus, 1 TB/s is one terabyte per 2d.

Are you getting the full bandwidth? Find out with PRTG Network Monitor!
Are your service providers giving you the full bandwidth? Is your bandwidth stable? Are there any bandwidth hogs? Detect out past using the professional Bandwidth Monitoring Tool PRTG.
- Unlimited version of PRTG for 30 days
- Afterwards 30 days, PRTG reverts to a complimentary version
- Or, you lot can upgrade to a paid license someday
Measuring bandwidth
Measuring bandwidth is typically done using software or firmware, and a network interface. Common bandwidth measuring utilities include the Exam TCP utility (TTCP) and PRTG Network Monitor, for example.
TTCP measures throughput on an IP network between two hosts. One host is the receiver, the other the sender. Each side displays the number of bytes transmitted and the fourth dimension for each packet to complete the ane-way trip.
PRTG provides a graphical interface and charts for measuring bandwidth trends over longer periods of time, and can measure traffic betwixt dissimilar interfaces.
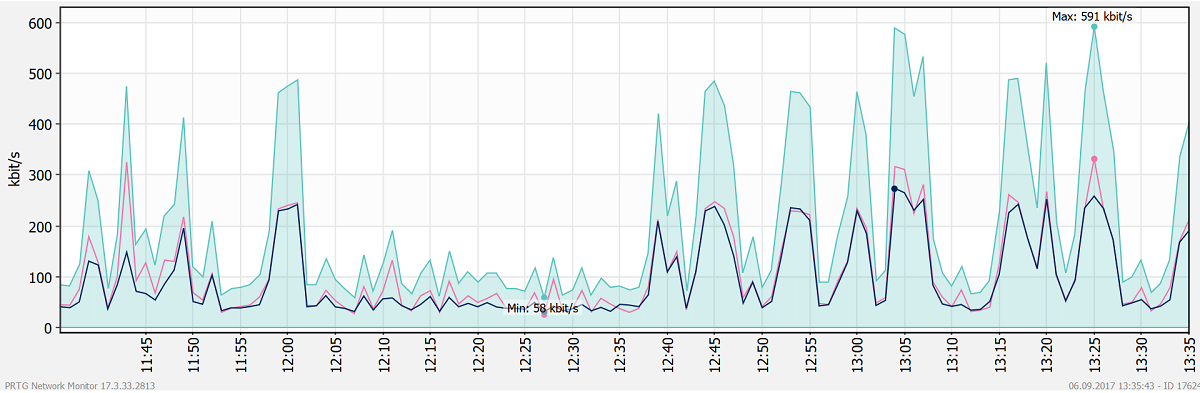
Typically, to measure bandwidth, the total amount of traffic sent and received beyond a specific period of time is counted. The resulting measurements are then expressed every bit a per-2d number.
Some other method of measuring bandwidth is to transfer a file, or several files, of known size and count how long the transfer takes. The result is converted into bps by dividing the size of the files past the amount of fourth dimension the transfer required. Most cyberspace speed tests utilize this method to summate the connexion speed of a user'south estimator to the internet.
While there is no style to measure total available bandwidth, at that place are many means to define measured bandwidth, depending on the need.
Theoretical maximum – The highest transmission rate under platonic circumstances. The theoretical maximum transfer rate cannot exist achieved in actual installations. Typically, the theoretical maximum is but used for comparison as a way of determining how well a connexion is functioning compared to its theoretical maximum potential.
Constructive bandwidth – The highest reliable transmission charge per unit. E'er lower than the theoretical maximum. Sometimes considered the all-time usable bandwidth. Necessary for understanding the amount of traffic a connection tin can support.
Throughput – The average charge per unit of successful data transfer; useful for agreement the typical or usual speed of a connection. Throughput is the size of the transfer divided by the time information technology takes for the transfer to consummate. Measured in bytes per 2d, throughput can be compared to the effective bandwidth and the theoretical maximum equally a style of determining how well the connection is performing.
Goodput – Measures the amount of useful information that is transferred, excluding undesirable data such as packet retransmissions or protocol overhead. Goodput is calculated by dividing the size of the transferred file past the amount of time the transfer took.
Total transfer method – Counts all traffic across a catamenia of set fourth dimension, typically a calendar month. This is most useful for billing based on how much bandwidth is used.
95th percentile method – To avoid having bandwidth measurements skewed by spikes in usage, carriers often use the 95th percentile method. The idea is to continuously measure bandwidth usage over time, then remove the top 5 percent of apply. This is useful for billing based on how much bandwidth is 'normally' used in a set menses.
In existent world networks, bandwidth varies over fourth dimension depending on use and network connections. As a result, a single bandwidth measurement says very piffling near bodily bandwidth usage. A series of measurements can be more than useful when determining averages or trends.

Bandwidth vs. speed vs. throughput
There are many ways to think virtually the flow of data in a network. The speed of a network is divers as the bit rate of the excursion, determined past the physical signal speed of the medium.
Bandwidth is how much of the physical excursion's capacity can be used to transmit data and is determined past how much of the network capacity is available based on the connection. While a Gigabit Ethernet network connectedness would allow for i Gbps, the bandwidth available to a computer connected by a Fast Ethernet bill of fare would just be 100 Mbps.
Throughput is the rate of successful transmission, while bandwidth is a calculation of the corporeality of data that passes the network interface, regardless of whether the data results in a successful transmission. As such, throughput is always lower than bandwidth.
Why measure out bandwidth
At that place are several reasons to measure bandwidth. Low usable bandwidth compared to the theoretical maximum bandwidth may be indicative of network issues, peculiarly if there are widely different usable bandwidths from different parts of a network that are designed to operate the aforementioned.
Additionally, measuring bandwidth is necessary to ensure that any paid connections are living up to their promise. Dwelling house users may run an online bandwidth test such as the DSLReports speed test to see but how much of that "up to 40 Mb/s" connection their internet access provider (Isp) charges them for they really get to use. Corporate connections might be better served past measuring throughput between offices connected by a carrier-leased line connexion.
Bandwidth direction
In order to implement proper bandwidth direction, or Quality of Service (QoS) controls, i must outset understand what bandwidth is used. One time determined, a continuous measurement will ensure that all users go the necessary bandwidth.
Bandwidth throttling
One time bandwidth usage patterns are understood, and if specific users or applications are degrading network performance for others, tools can be used to limit the amount of bandwidth they are using.
Bandwidth maximums
Some types of connections have a maximum defined bandwidth. Actual bandwidth depends on many factors including environment, cabling, and usage, and is usually less than the theoretical maximum.
Wired bandwidth standards for connections
| Dialup Modem | 56 kbps |
| T1 (Digital leased landline connectedness) | ane.544 Mbps |
| E1 (Digital leased landline connection European) | 2.048 Mbps |
| Asynchronous DSL | iv Mbps |
| Ethernet | 10 Mbps |
| T3 (Digital leased landline connection) | 44.763 Mbps |
| VDSL | 55 Mbps |
| VDSL two | 100 Mbps |
| Fast Ethernet | 100 Mbps |
| OC3 (Ficer optic leased landline connection) | 155 Mbps |
| OC 12 (Ficer optic leased landline connection) | 622 Mbps |
| Gigabit Ethernet | 1000 Mbps or 1 Gbps |
| VSDL 2 Vplus | 300 Mbps |
| 10 Gigabit Ethernet | 10 Gbps |
| 100 Gigabit Ethernet | 100 Gbps |
Wireless network standard maximum download speeds
Wireless network connexion speeds vary widely based on the atmospheric condition of the connection. The numbers below are the maximum bandwidth speeds according to the standard or specification.
| 802.11b | 11 Mbps |
| 802.11g | 54 Mbps |
| 802.11n | 600 Mbps |
| 802.11ac | 600 Mbps |
| 3G - HSPA | seven.two Mbps |
| 3G - HSPA+ | 21 Mbps |
| 3G - DC-HSPA+ | 42 Mbps |
| 4G - LTE | 100 Mbps |
| 5G (proposed) | 1 Gpbs (or higher) |
WiFi 802.11bf: New applications for wireless devices
The WiFi standard 802.11bf will not just be used for communication simply besides as a complete sensing epitome. This will expand the possibilities of WiFi and e.g. detect which people or objects are moving within its range of movement.
The upcoming version can be used in industrial and commercial environments in manufacturing systems, corporate networks, and test and measurement equipment.
Purchasing bandwidth
Bandwidth is most often purchased from telecommunications companies. Most consumer bandwidth is sold as "up to" meaning that the customer may get up to forty MB/s, but not e'er have that speed while using the connection. Speeds may be higher or lower at different times of the day or under different circumstances. Corporate bandwidth is as well typically purchased from telecommunications companies. Still, many corporate agreements come with contractual performance measures that must be met, including a minimum usable bandwidth, minimum uptime, and other metrics.
Additionally, bandwidth metering may be used to accuse for specific usage rather than a total connexion. For example, a website owner may pay the website host but for the amount of bandwidth used by that specific website over a period of time, such as a monthly billing period.
Bandwidth issues
Too fiddling bandwidth
While modernistic protocols are pretty expert about non losing whatever packets, limited bandwidth tin nonetheless cause operations to be besides long to consummate, resulting in timeouts or other problems. These issues can cause application errors or database errors. When backing up or copying data over a network, too picayune bandwidth tin cause backups to take too long, oftentimes running into other batch processes, or fifty-fifty primary working hours.
In addition, users relying on a connection with too little bandwidth may detect long lag times between when they do something, like click a button, and the response to that action. In the example of waiting for data or other data to load, too little bandwidth can cause operations to have a long time, or even crusade users to requite upward waiting.
For users attempting to make phone calls over a network, such equally Voice over Net Protocol (VoIP), having too little bandwidth results in lower quality calls. About VoIP systems reduce the fidelity of a telephone call based on the available bandwidth. If there is not enough bandwidth, the call may sound "tinny" or "echo-y". If the quality is bad enough, in that location may be actual gaps in the phone call where parts of the conversation are missed.
Video calls require even more bandwidth. Video calls fabricated without the necessary bandwidth will not simply outcome in bad sound quality, but also low quality or jittery video.
For net users, the United States Federal Communications Committee (FCC) recommends a minimum bandwidth of four Mbps for adequate performance when streaming a video in HD quality. Many video players will work with less bandwidth by "buffering", or downloading data ahead of when information technology is actually displayed. If the connection is too slow, users will either take to wait a long time before the video starts while the system buffers a lot of data, or the video may stop all of a sudden when the system runs out of buffered video to play.
Gamers are oftentimes frustrated by express bandwidth as well. While playing against other players online, players with faster connections see what is happening quicker, and the data about their reactions is transmitted and received faster. The FCC recommends a minimum download speed of 4 Mbps for Online Multiplayer Gaming in Hard disk.
| | 0.5 Mbps |
| Web Browsing | 0.5 Mbps to 1.0 Mbps |
| Streaming Music | 0.5 Mbps |
| Phone Calls (VoIP) | 0.v Mbps |
| Streaming Videos | 0.7 Mbps |
| Streaming Movies (Non-HD) | 1.5 Mbps |
| Streaming Hard disk drive Quality Movies | 4 Mbps |
| Basic Video Conferencing | 1 Mbps |
| Hd Video Conferencing | 4 Mbps |
| Cyberspace Connected Game Console | ane Mbps |
| Online Multiplayer Hard disk drive Gaming | iv Mbps |
Table of FCC minimum required download speed
Too much bandwidth
There a few technical problems caused past too much bandwidth. Higher chapters bandwidth, all the same, typically costs more than. Thus, as well much bandwidth may not exist toll constructive.
Latency
Network blueprint and infrastructure tin create bandwidth problems as well. Latency measures the delays on a network that may exist causing lower throughput or goodput. A low latency network has brusk delays, while a high latency network has longer delays. High latency prevents data from fully using the network's capabilities, therefore decreasing the bandwidth.
Troubleshooting bandwidth issues
Finding and remedying bandwidth problems helps amend network performance without costly upgrades.
Ping and traceroute
Tools such as Ping and traceroute can assistance troubleshoot bones issues.
Pinging a examination server, for example, will render data on how quickly data can be sent and received, every bit well as average circular trip times. High ping times indicate higher latency in the network.
The traceroute tool can help determine if there are too many individual network connections, or hops, along the connection path. In addition, traceroute returns the time taken by each hop. A longer time on a single hop may pinpoint the source of an issue.

TTCP
TTCP measures the time it takes for information to travel from ane network interface to another with a receiver on the other terminate. This eliminates the render trip from the adding and may help pinpoint issues rapidly. If the measured bandwidth is less than expected, farther measurements can isolate the effect. Does a measurement to some other interface on the aforementioned network work faster? If so, where is the difference betwixt the two systems? Past continually measuring bandwidth, administrators can target the bottlenecks in the network.
PRTG Network Monitor
With its data gathering and graphing interface, PRTG can as well help troubleshoot bandwidth problems that are not related to design. For example, past measuring bandwidth usage over time, information technology may be determined that certain users or applications are sometimes using higher amounts of bandwidth and causing network congestion and slowing network responsiveness and cyberspace speed for other users.
Find out more than about bandwidth monitoring with PRTG >

Are you getting the full bandwidth? Find out with PRTG Network Monitor!
Are your service providers giving you the full bandwidth? Is your bandwidth stable? Are there any bandwidth hogs? Discover out by using the professional Bandwidth Monitoring Tool PRTG.
- Unlimited version of PRTG for 30 days
- Afterward 30 days, PRTG reverts to a gratuitous version
- Or, you can upgrade to a paid license anytime
This is a curt video well-nigh bandwidth monitoring
References
marchantallis1956.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.paessler.com/it-explained/bandwidth
0 Response to "What Term Refers to the Maximum Speed at Which Data Can Be Transferred?"
Post a Comment